Paper in Action
AI CodeReview
BitsAI-CR: Automated Code Review via LLM in Practice
CodeRAG
CodeRAG: Supportive Code Retrieval on Bigraph for Real-World Code Generation
论文讲解:https://developer.volcengine.com/articles/7496711933538598963
现实世界代码生成的困境
当前主流大语言模型(LLM, Large Language Model)在生成独立代码片段时表现优异,但在处理真实项目中的代码生成任务时面临三大挑战。
• 首先,代码库依赖关系复杂,包括跨文件调用、继承关系等结构化关联。例如,在金融领域项目中,一个交易处理函数可能需要调用分布在 5-6 个不同文件中的验证、计算和日志记录模块。 • 其次,专业领域知识缺失问题突出,实验数据显示 LLM 在生成涉及加密算法或金融衍生品定价等专业代码时,准确率比通用场景下降 35-40%。 • 最后,上下文窗口限制导致模型无法完整加载整个代码库,即使使用 32k tokens 的上下文窗口,也只能覆盖典型 Java 项目 15-20%的代码量。
现有解决方案的不足
传统检索增强生成(RAG, Retrieval-Augmented Generation)方案存在明显局限。
• 基于文本相似度的方法(如 BM25)会忽略代码结构特征,在 DevEval 基准测试中,对包含继承关系的代码检索准确率仅为 42%。 • 图查询方法(如 CodeXGraph)受限于固定语法规则,无法处理动态语言特性,在 Python 装饰器等高级语法场景下失效率达 60%。 • Agent方法(如 CodeAgent)缺乏系统性知识检索机制,实验显示其生成代码与项目已有代码的接口匹配成功率不足 30%。
人类编程的启发
开发者通常遵循 “需求分析 → 依赖定位 → 参考实现 → 调试优化” 的工作流。CodeRAG 创新性地模拟这个过程:
• 通过构建需求图(Requirement Graph)捕捉功能逻辑关系 • 建立 DS-Code 图(Dependency-Semantic Code Graph)建模代码结构 • 再通过双图映射实现精准知识检索。
什么是 CodeRAG?
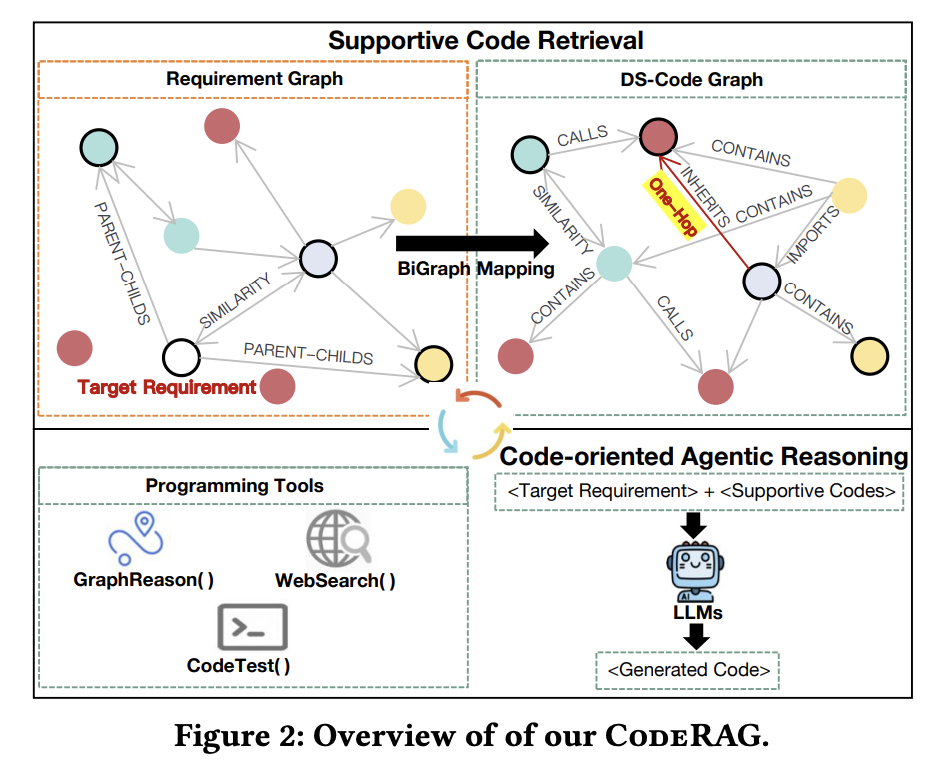
CodeRAG 的四大核心组件:需求图谱(Requirement Graph)、DS-Code 图(Dependency-Semantic Code Graph)、双图映射引擎(Bigraph Mapping)和 Agentic 代码生成。
A Deep Dive into Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Code Completion: Experience on WeChat
Code completion, a crucial(至关重要的) task in software engineering that enhances developer productivity, has seen substantial(大量的) improvements with the rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs). In recent years, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has emerged as a promising(前景很好的) method to enhance the code completion capabilities of LLMs, which leverages relevant context from codebases without requiring model retraining.
While existing studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of RAG on public repositories and benchmarks, the potential distribution shift between open-source and closed-source codebases presents unique challenges that remain unexplored.
To mitigate the gap, we conduct an empirical(实证的) study to investigate the performance of widely-used RAG methods for code completion in the industrialscale codebase of WeChat, one of the largest proprietary software systems. Specifically, we extensively explore two main types of RAG methods, namely identifier-based RAG and similaritybased RAG, across 26 open-source LLMs ranging from 0.5B to 671B parameters.
For a more comprehensive analysis, we employ different retrieval techniques for similarity-based RAG, including lexical and semantic retrieval. Based on 1,669 internal repositories, we achieve several key findings:
- both RAG methods demonstrate effectiveness in closed-source repositories, with similarity-based RAG showing superior performance
- the effectiveness of similarity-based RAG improves with more advanced retrieval techniques, where BM25 (lexical retrieval) and GTE-Qwen (semantic retrieval) achieve superior performance
- the combination of lexical and semantic retrieval techniques yields optimal results, demonstrating complementary strengths. Furthermore, we conduct a developer survey to validate the practical utility of RAG methods in real-world development environments.
代码静态分析
Lint is the computer science term for a static code analysis tool used to flag programming errors, bugs, stylistic errors and suspicious constructs. The term originates from a Unix utility that examined C language source code. A program which performs this function is also known as a “linter” or “linting tool”.
例如:C++ 中使用的 Cpplint,Cpplint 是一个 Python 编写的基于 Google 代码规范的检测工具。它只是一个代码风格检测工具,其并不对代码逻辑、语法错误等进行检查。
如何减少误报?莱斯定理 Rice’s theorem
In computability theory, Rice’s theorem states that all non-trivial semantic properties of programs are undecidable. A semantic property is one about the program’s behavior (for instance, “does the program terminate for all inputs?”), unlike a syntactic property (for instance, “does the program contain an if-then-else statement?”). A non-trivial property is one which is neither true for every program, nor false for every program.
对于计算机程序(更精确地说,是图灵机)而言,任何关于程序行为(语义)的、非平凡的(non-trivial)属性,都是不可判定的(undecidable)。
非平凡属性:指这个属性不是所有程序都具备的(恒真),也不是所有程序都不具备的(恒假)。平凡属性是可判定的(直接回答“是”或“否”就行)。
不可判定:指不存在一个通用算法(一个能处理任何程序的程序),能够精确地、总是正确地判断任意给定的程序是否具有该属性。
计算机程序的行为极其复杂且不可预测。你不可能编写出一个“万能检查器”,让它只通过阅读任何程序的源代码,就能百分之百可靠地回答出关于这个程序运行时行为(比如它会不会出错、算得对不对、会不会停)的任何非平凡问题。 这是计算理论中一个非常基础且重要的不可行性结果,深刻影响了程序语言理论、软件工程和形式化方法的发展。